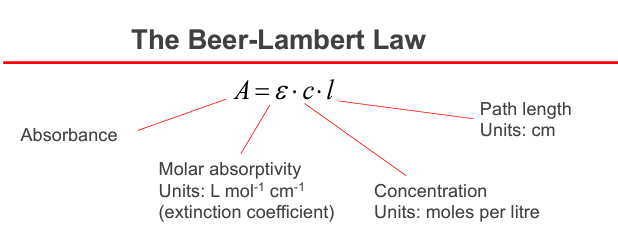
Spectroscopy: the act of taking a spectrum which involves resolving electromagnetic
radiation into component wavelengths
Spectrum: Plot of radiant intensity or absorption vs wavelength
Chromophore: an identifiable part of the molecule which gives rise to a characteristic absorption
electromagnetic radiation can be absorbed or emitted if the difference between energy levels is the same as the
energy of the photon
 Radiative Relaxation:
Radiative Relaxation: energy gained or lost as radiation (energy is lost by emission of a photon)
Non Radiative Relaxation: energy gained or lost in other ways
Vibrational Relaxation: molecule drops in energy to the lowest vibrational energy of an excited state
Internal Conversion: molecule relaxes from the lowest vibrational level of one electronic state to upper
vibrational levels of a lower electronic state
External Conversion: molecule relaxes as energy passes to solvent via collisions
Intersystem crossing (ISC): spin of electron is reversed, hence molecules goes from singlet (spins paired)
to triplet state (spins unpaired)
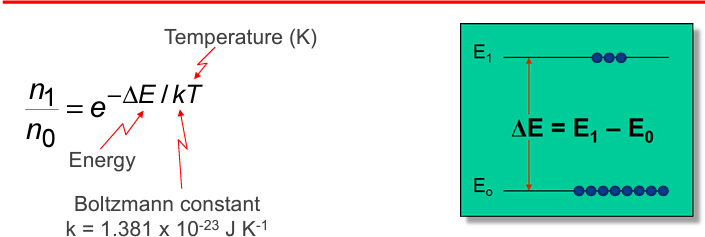
Boltzmann Distribution for electrons in 2 states:
the greater the difference between n1 and n2, the greater the size of delta E and therefore lower wavelength and
higher frequency.
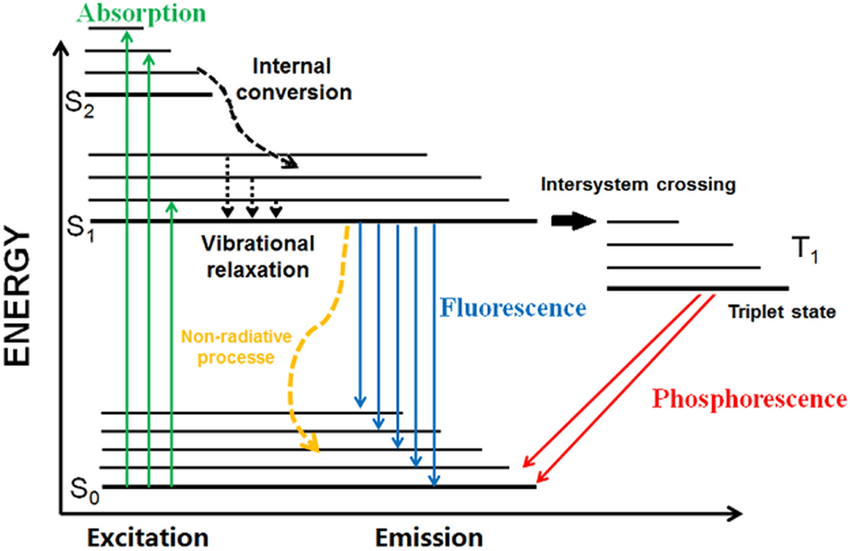
fluorescence vs phosphorescence
fluorescence involves exciting an electron to a higher energy state, then relaxing to the lowest excited electronic
transition state (Kasha's rule), before emitting a photon, taking it to ground state.
phosphorescence is the same as fluorescence, but the electron state is flipped, causing the probability of it
emitting a photon and relaxing to ground state to decrease.
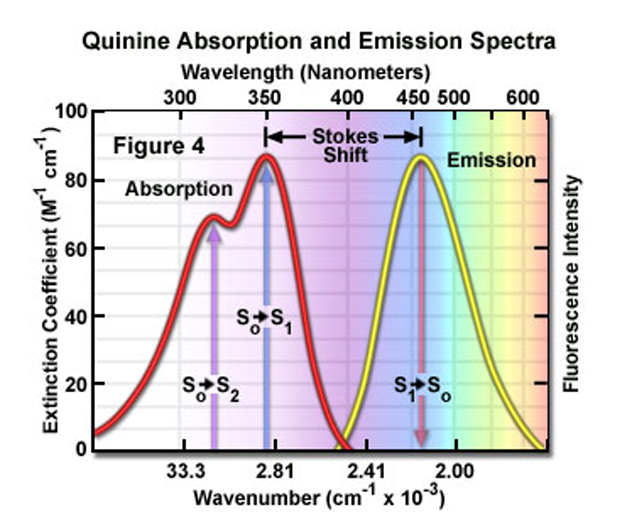
Quinine absorbs in the ultraviolet region and emits in the blue/green region of the visible section. The stokes shift is the distance between
the peaks of the absorbtion and emisssions spectrum.
fluorescence intensity is proportional to the concenetration of the concentration of the substance that is fluorescing.
The Quantum Yield = # photons emitted / # photons absorbed
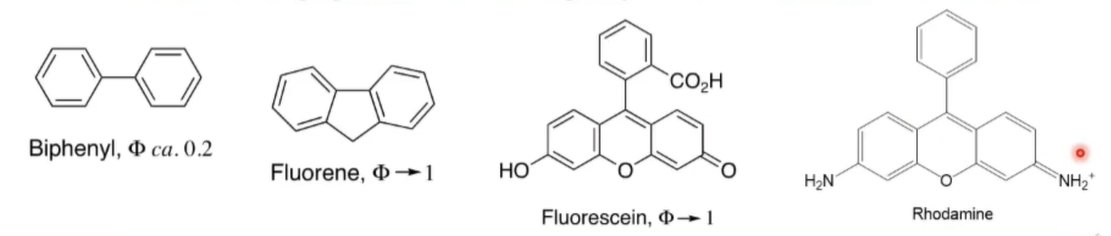
increases with increasing number of fused aromatic rings and extended conjugation and rigidity of molecular framework
molecules that fluoresce and have a high quantum yield emit strong fluorescence even at low concentrations.
absorbtion of infrared light is enough to cause the bonds of molecules to bend or stretch.
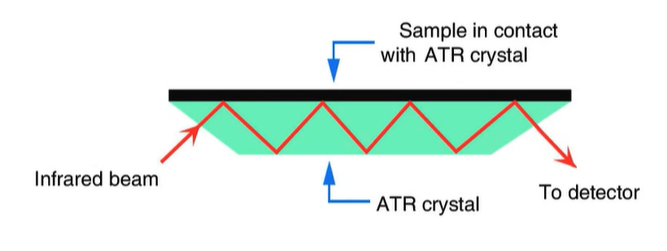
Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR)
> ATR crystals have a high reflective index (diamond, germanium, zinc selenide)
> easier sample preparation
> allows solids, liquids, gels, composites
> solids are usually compressed to ensure good contact with the ATR crystal
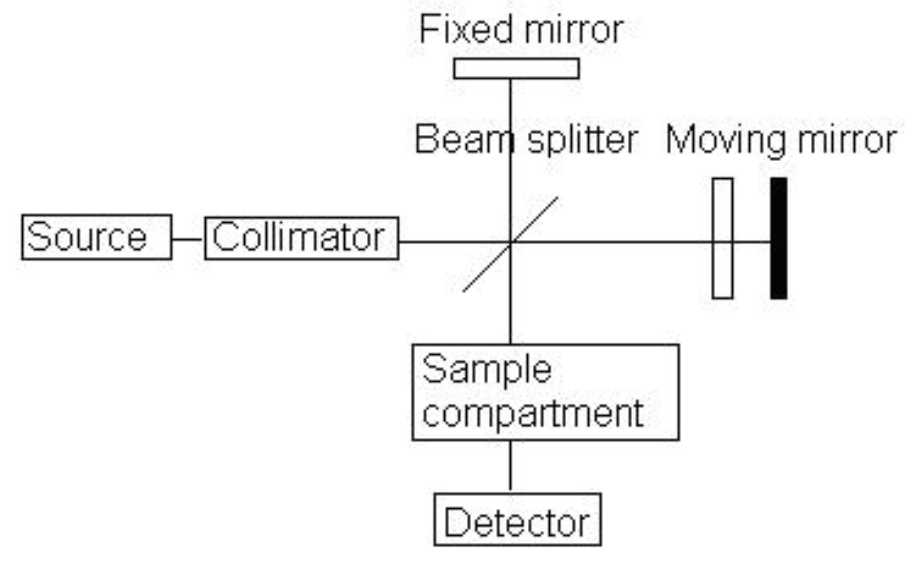
 Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
> all IR frequencies are recorded at the same time
> signal is detected as an interference pattern
> requires a computer to perform a fourier transformation to convert the interference pattern to a conventional spectrum
> high sensitivity
> excellent resolution
> rapid acquisition
> more complex instrumentation
> higher cost
 Sample preparation
Sample preparation
> solid, liquids and gases
> must be on plates that don't absorb IR light (KBR and NaCl are IR transparent)
> solvents must be IR transparent
Infrared Spectroscopy
the wavelength window for IR spectroscopy is 2500 - 25000nm
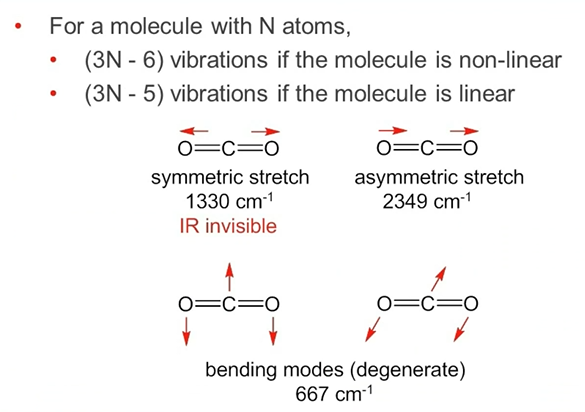
the energy difference between vibrational levels depend on:
> the masses of atoms involved in the vibration
> the strength of bonds involved in the vibration
> the shape of the molecule
Hookes Law: F = -ky
where F = force, k = spring constant, y = displacement
stronger bonds have a bigger k. triple bonds > double bonds > single bonds
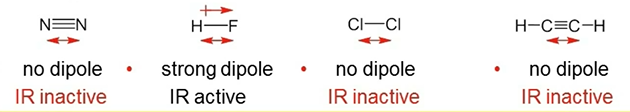
Selection Rule for IR
vibration must involve a change in the dipile moment along the bond being stretched.
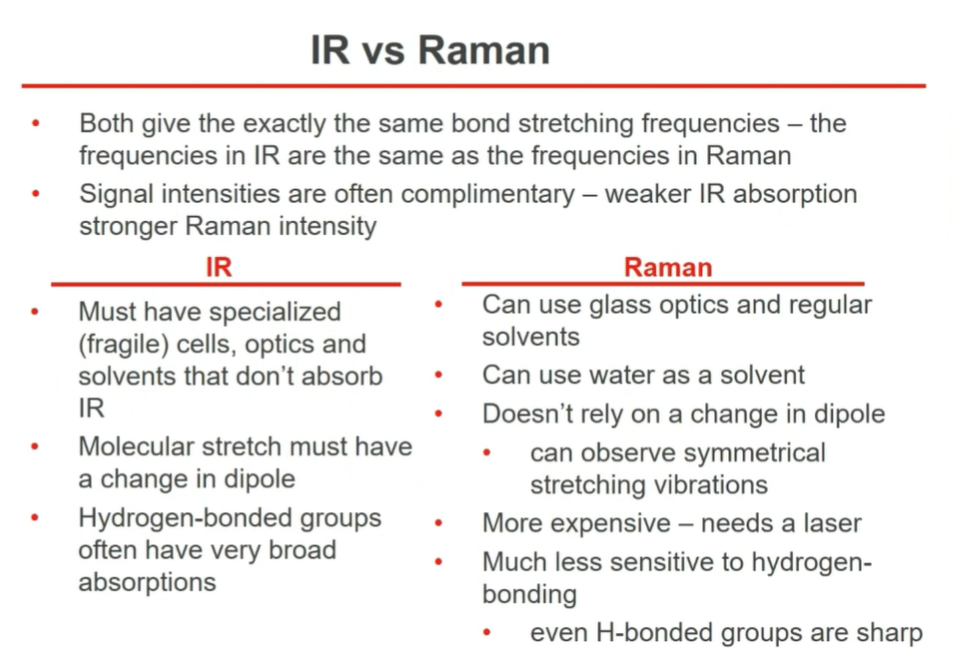
 Raman Spectroscopy
Raman Spectroscopy
> peaks are up as it measures scattered light
absorbtion of radio light is enough to cause the electrons to flip states.
nuclei with no spin are NMR inactive
 Radiative Relaxation: energy gained or lost as radiation (energy is lost by emission of a photon)
Radiative Relaxation: energy gained or lost as radiation (energy is lost by emission of a photon)

 Quinine absorbs in the ultraviolet region and emits in the blue/green region of the visible section. The stokes shift is the distance between
the peaks of the absorbtion and emisssions spectrum.
Quinine absorbs in the ultraviolet region and emits in the blue/green region of the visible section. The stokes shift is the distance between
the peaks of the absorbtion and emisssions spectrum.
 fluorescence intensity is proportional to the concenetration of the concentration of the substance that is fluorescing.
fluorescence intensity is proportional to the concenetration of the concentration of the substance that is fluorescing.

 Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
 Sample preparation
Sample preparation