Programming Fundamentals
Objectives
- More complex linked lists
- Practice working with lists of lists
Feedback Week!
In this week's lab, your tutors will go around the class and give you one on one feedback on some code you've written in a previous week.
This is also an opportunity for you to ask any questions you might have about the course content so far!
So, if you'd like, have a think about if there's any particular exercise you'd like to receive feedback for, or any particular content you'd like to ask about.
Reminder: Help sessions
Help sessions are running this week!
These are one of the best ways for you to get one on one help with a tutor for any course content (including Lab Exercises and Assignments).
For the dates and times of the help sessions, see the Help Session Timetable.
To join a help session, or for more information, see the COMP1511 Help Session Microsoft Teams.
For face-to-face help sessions, the lab map can be found Here.
Activities To Be Completed
The following is a list of all the activities available to complete this week...
Worth 1 mark(s) in total:
- debug_remove_second_last
- list_create
- list_increasing
- list_delete_first
- list_get_middle
Worth 1 mark(s) in total:
- list_delete_contains_string
- list_delete_highest
Worth 0.5 mark(s) in total:
- lists_diagonal
- musical_chairs
For your interest, but not for marks:
- student_becomes_teacher_week9
Problem sets are capped at 15 marks (there are 4 possible bonus marks from the three-dot exercises that can bring you up to a total of 15 if you missed out on any other marks in the one- or two-dot exercises).
Completing just the one and two-dot exercises every week can give you the full 15 marks needed in this component.
For more details, see the course outline.
Preparation
Before the lab you should re-read the relevant lecture slides and their accompanying examples.
When attempting the following exercises, make sure to read the whole exercise, including any hints and assumptions that may make the exercise easier.
Exercise
(●◌◌)
:
Debugging - List remove second last
Download debug_remove_second_last.c here
Or, copy these file(s) to your CSE account using the following command:
1511 fetch-activity debug_remove_second_last
Debugging Tips!
Some debugging tips for you:
- dcc output - as you run into issues, dcc will point out where the errors are. Remember that dcc gives you the line number the issue is on, and will give some sort of explanation. Make sure you read everything dcc gives you. Sometimes we get “errors carried forward”, so find your first error, fix that, then recompile.
- print statements - sometimes it can be handy to see if the flow of your code puts you in the spot you expect it to be (ie. inside the right if statement, or going through a loop the correct amount of times). A quick way you can check this is by putting print statements in your code for testing purposes, like
"the value of x is %d and y is %d". This lets you check that you got against what you expected. - COMP1511 debugging guide
The Task
This program takes in a linked list via command line arguments. Then, it attempts to remove the second last element of the list previously created via the delete_second_last function.
For example if the existing list is 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4-> X, after calling the delete_second_last function on the list it becomes 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> X. Note, the node containing the value 3 is removed from the list since it is the second last element in the list.
Currently the program has some issues it is your job to figure them out and fix the code.
Note: You should only need to modify the delete_second_last function to fix the program.
Examples
dcc debug_remove_second_last.c -o debug_remove_second_last ./debug_remove_second_last 1 2 3 4 5 6 Original list: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] Modified list: [1, 2, 3, 4, 6] ./debug_remove_second_last 1 2 3 Original list: [1, 2, 3] Modified list: [1, 3] ./debug_remove_second_last 1 2 Original list: [1, 2] Modified list: [2] ./debug_remove_second_last 1 Original list: [1] Modified list: [] ./debug_remove_second_last Original list: [] Modified list: []
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications
- You may assume all command line arguments will be integers
1511 style debug_remove_second_last.c
When you think your program is working,
you can use autotest
to run some simple automated tests:
1511 autotest debug_remove_second_last
When you are finished working on this exercise,
you must
submit your work by running give:
give cs1511 lab09_debug_remove_second_last debug_remove_second_last.c
You must run give
before Monday 15 April 20:00
to obtain the marks for this lab exercise.
Note that this is an individual exercise,
the work you submit with give must be entirely your own.
Exercise
(●◌◌)
:
Create a Linked List from Command Line Arguments, and then Free it
Download list_create.c here
Or, copy these file(s) to your CSE account using the following command:
1511 fetch-activity list_create
Your task is to add code to these functions in list_create.c:
// Create linked list from argument values
struct node *arguments_to_list(int argc, char *argv[]) {
// TODO: Complete this function and change the line below
return NULL;
}
// Free the linked list from memory
void free_list(struct node *head) {
// TODO: Complete this function
}
Complete the program list_create.c. The program converts command line arguments into a linked list, prints out the linked list, and then frees the linked list. It is your job to complete the function that creates the linked list (arguments_to_list) and the function that frees the linked list (free_list).
Examples
dcc list_create.c -o list_create ./list_create 5 3 2 9 4 1 5 -> 3 -> 2 -> 9 -> 4 -> 1 -> X ./list_create I love this COMP1511 exercise!! I -> love -> this -> COMP1511 -> exercise!! -> X ./list_create 8915 10563 10821 9979 14640 8433 6894 125 8915 -> 10563 -> 10821 -> 9979 -> 14640 -> 8433 -> 6894 -> 125 -> X ./list_create X
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications
- Any length of command line arguments can be given
- Do not change the supplied
mainfunction. Only yourarguments_to_listandfree_listfunction will be tested
1511 style list_create.c
When you think your program is working,
you can use autotest
to run some simple automated tests:
1511 autotest list_create
When you are finished working on this exercise,
you must
submit your work by running give:
give cs1511 lab09_list_create list_create.c
You must run give
before Monday 15 April 20:00
to obtain the marks for this lab exercise.
Note that this is an individual exercise,
the work you submit with give must be entirely your own.
Exercise
(●◌◌)
:
Check whether a Linked List is in Increasing Order
Download list_increasing.c here
Or, copy these file(s) to your CSE account using the following command:
1511 fetch-activity list_increasing
Your task is to add code to this function in list_increasing.c:
int increasing(struct node *head) {
// PUT YOUR CODE HERE (change the next line!)
return 42;
}
increasing is given one argument, head which is the pointer to the first
node in a linked list.
Add code to increasing so that its returns 1 if the list is in increasing
order - the value of each list element is larger than the element before.
For example if the linked list contains these 8 elements:
1, 7, 8, 9, 13, 19, 21, 42
increasing should return 1 because it is increasing order
Testing
list_increasing.c also contains a main function which allows you to test
your increasing function.
This main function:
- converts the first set of read integers to a linked list,
- assigns a pointer to the first node in the linked list to
head, - calls
list_increasing(head)and - prints the result.
Do not change this main function. If you want to change it, you have misread
the question.
Your list_increasing function will be called directly in marking. The main
function is only to let you test your list_increasing function
Examples
dcc list_increasing.c -o list_increasing ./list_increasing How many numbers in initial list?: 9 1 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 256 1 ./list_increasing How many numbers in initial list?: 6 2 4 6 5 8 9 0 ./list_increasing How many numbers in initial list?: 6 13 15 17 17 18 19 0 ./list_increasing How many numbers in initial list?: 2 2 4 1 ./list_increasing How many numbers in initial list?: 1 42 1 ./list_increasing How many numbers in initial list?: 0 1
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications
increasingshould return a single integerincreasingshould not change the linked list it is given. Your function should not change the next or data fields of list nodesincreasingshould not use arraysincreasingshould not callmallocincreasingshould not call scanf (orgetcharorfgets)- You can assume the linked list only contains positive integers
increasingshould not print anything. It should not callprintf- Do not change the supplied
mainfunction. It will not be tested or marked.
1511 style list_increasing.c
When you think your program is working,
you can use autotest
to run some simple automated tests:
1511 autotest list_increasing
When you are finished working on this exercise,
you must
submit your work by running give:
give cs1511 lab09_list_increasing list_increasing.c
You must run give
before Monday 15 April 20:00
to obtain the marks for this lab exercise.
Note that this is an individual exercise,
the work you submit with give must be entirely your own.
Exercise
(●◌◌)
:
Delete First Element from a Linked List
Download list_delete_first.c here
Or, copy these file(s) to your CSE account using the following command:
1511 fetch-activity list_delete_first
Your task is to add code to this function in list_delete_first.c:
//
// Delete the first node in list.
// The deleted node is freed.
// The head of the list is returned.
//
struct node *delete_first(struct node *head) {
// PUT YOUR CODE HERE (change the next line!)
return NULL;
}
Note list_delete_first.c uses the following familiar data type:
struct node {
struct node *next;
int data;
};
delete_first is given one argument, head which is the pointer to the first
node in the linked list
Add code to delete_first so that it deletes the first node from list
delete_first should return a pointer to the new first node in the list
If the list is now empty, delete_first should return NULL
delete_first should call free to free the memory of the node it deletes
For example if the linked list contains these 8 elements:
16, 7, 8, 12, 13, 19, 21, 12
delete_first should return a pointer to a list with these elements:
7, 8, 12, 13, 19, 21, 12
Hint: This task should only require a few lines of code
Testing
list_delete_first.c also contains a main function which allows you to test
your delete_first function. It converts the inputs to a linked list,
calls delete_first and then prints the result.
Do not change this main function. If you want to change it, you have misread
the question.
Your delete_first function will be called directly in marking. The main
function is only to let you test your delete_first function
Examples
dcc list_delete_first.c -o list_delete_first ./list_delete_first Total numbers: 8 16 7 8 12 13 19 21 12 [7, 8, 12, 13, 19, 21, 12] ./list_delete_first Total numbers: 6 2 4 6 2 4 6 [4, 6, 2, 4, 6] ./list_delete_first Total numbers: 1 42 [] ./list_delete_first Total numbers: 0 []
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications
delete_firstshould callfreeto free the memory for the node it deletesdelete_firstshould not change the data fields of list nodesdelete_firstshould not use arraysdelete_firstshould not callmallocdelete_firstshould not call scanf (orgetcharorfgets)delete_firstshould not print anything. It should not callprintf- Do not change the supplied
mainfunction. It will not be tested or marked
1511 style list_delete_first.c
When you think your program is working,
you can use autotest
to run some simple automated tests:
1511 autotest list_delete_first
When you are finished working on this exercise,
you must
submit your work by running give:
give cs1511 lab09_list_delete_first list_delete_first.c
You must run give
before Monday 15 April 20:00
to obtain the marks for this lab exercise.
Note that this is an individual exercise,
the work you submit with give must be entirely your own.
Exercise
(●◌◌)
:
Get the middle element from a Linked List
Download list_get_middle.c here
Or, copy these file(s) to your CSE account using the following command:
1511 fetch-activity list_get_middle
Your task is to add code to this function in list_get_middle.c:
// Return middle element of a linked list
// if list contains [6,7,8,9,10] 8 is returned
// if a list has even number of elements, first of middle two elements returned
// if list contains [1,2,3,4] 2 is returned
// list can not be empty
int get_middle(struct node *head) {
// PUT YOUR CODE HERE (change the next line!)
return 42;
}
get_middle is given one argument, head which is the pointer to the first
node in a linked list.
Add code to get_middle so that its returns the middle value of the list.
If the list an even number of elements the first of the 2 elements in the
middle of the list should be returned.
For example if the linked list contains these 8 elements:
1, 7, 8, 9, 13, 19, 21, 42
get_middle should return 9 because 9 and 13 are the middle two elements
And, for example if the linked list contains these 5 elements:
1, 2, 8, 1, 42
get_middle should return 8 because it is the middle element.
get_middle can assume the list is not empty.
Testing
list_get_middle.c also contains a main function which allows you to test
your get_middle function.
This main function:
- converts the inputs to a linked list,
- assigns a pointer to the first node in the linked list to
head, - calls
list_get_middle(head)and - prints the result.
Do not change this main function. If you want to change it, you have misread
the question.
Your list_get_middle function will be called directly in marking. The main
function is only to let you test your list_get_middle function
Examples
dcc list_get_middle.c -o list_get_middle ./list_get_middle How many numbers in initial list?: 9 1 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 256 16 ./list_get_middle How many numbers in initial list?: 6 2 4 6 5 8 9 6 ./list_get_middle How many numbers in initial list?: 5 13 15 17 19 18 17 ./list_get_middle How many numbers in initial list?: 2 42 4 42 ./list_get_middle How many numbers in initial list?: 1 42 42
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications
get_middleshould return a single integerget_middlecan assume the list has at least one elementget_middleshould not change the linked list it is given Your function should not change the next or data fields of list nodesget_middleshould not use arraysget_middleshould not callmallocget_middleshould not call scanf (orgetcharorfgets)get_middleshould not print anything. It should not callprintf- Do not change the supplied
mainfunction. It will not be tested or marked
1511 style list_get_middle.c
When you think your program is working,
you can use autotest
to run some simple automated tests:
1511 autotest list_get_middle
When you are finished working on this exercise,
you must
submit your work by running give:
give cs1511 lab09_list_get_middle list_get_middle.c
You must run give
before Monday 15 April 20:00
to obtain the marks for this lab exercise.
Note that this is an individual exercise,
the work you submit with give must be entirely your own.
Exercise
(●●◌)
:
Delete first element containing a specific string from a linked list
Download list_delete_contains_string.c here
Or, copy these file(s) to your CSE account using the following command:
1511 fetch-activity list_delete_contains_string
Your task is to add code to this function in list_delete_contains_string.c:
// Delete the first node in the list containing the specific string
// The deleted node is freed.
// If no node contains the specified string, the list is not changed
// The head of the list is returned.
struct node *delete_contains(char string[MAX_SIZE], struct node *head) {
return NULL;
}
Note list_delete_contains.c uses the following familiar data type:
struct node {
struct node *next;
char data[MAX_SIZE];
};
delete_contains is given two argument, value and head.
datais a string with max size of 100 charactersheadis the pointer to the first node in a linked list
The function is designed to delete the first node in the linked list that contains a specific string.
Add code to delete_contains so that it deletes the first node in the linked
list that whose data field equals a specified string and returns a pointer to the new list.
-
If
datadoes not occur in the linked list, the list should not be changed. -
If
dataoccurs more than once in the linked list, only the first occurrence should be deleted. Note, if the list is now emptydelete_containsshould returnNULL.
delete_contains should call free to free the memory of the node it deletes.
Testing
list_delete_contains.c also contains a main function which allows you to
test your delete_contains function.
This main function:
- takes in command line arguments
- converts the command line inputs to a linked list,
- assigns a pointer to the first node in the linked list to
head, - reads a sstring from standard input and assigns it to
data, - calls
delete_contains(data, head)and - prints the result.
Do not change this main function. If you want to change it, you have misread
the question.
Your delete_contains function will be called directly in marking. The main
function is only to let you test your delete_contains function
dcc list_delete_contains_string.c -o list_delete_contains_string ./list_delete_contains_string cats sleep 16 to 18 hours per day Enter a string to delete: cats [sleep, 16, to, 18, hours, per, day] ./list_delete_contains_string the bumblebee bat is the worlds smallest mammal Enter a string to delete: bumblebee [the, bat, is, the, worlds, smallest, mammal] ./list_delete_contains_string Enter a string to delete: hello [] ./list_delete_contains_string there are parts of Africa in all four hemispheres Enter a string to delete: four [there, are, parts, of, Africa, in, all, hemispheres] ./list_delete_contains_string the most money ever paid for a cow in an auction was 1.3 million dollars Enter a string to delete: dollars [the, most, money, ever, paid, for, a, cow, in, an, auction, was, 1.3, million]
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications
delete_containsshould callfreeto free the memory for the node it deletesdelete_containsshould not change the data fields of list nodes.delete_containsshould not use arrays.delete_containsshould not callmalloc.delete_containsshould not call scanf (orgetcharorfgets).delete_containsshould not print anything. It should not callprintf.- Do not change the supplied
mainfunction. It will not be tested or marked.
1511 style list_delete_contains_string.c
When you think your program is working,
you can use autotest
to run some simple automated tests:
1511 autotest list_delete_contains_string
When you are finished working on this exercise,
you must
submit your work by running give:
give cs1511 lab09_list_delete_contains_string list_delete_contains_string.c
You must run give
before Monday 15 April 20:00
to obtain the marks for this lab exercise.
Note that this is an individual exercise,
the work you submit with give must be entirely your own.
Exercise
(●●◌)
:
Remove the Highest Elements
Download list_delete_highest.c here
Or, copy these file(s) to your CSE account using the following command:
1511 fetch-activity list_delete_highest
Your task is to add code to this function in list_delete_highest.c:
//
// Delete the node(s) in the list that contain the highest value
// The deleted node(s) are freed.
// The head of the list is returned.
//
struct node *delete_highest(struct node *head) {
// PUT YOUR CODE HERE (change the next line!)
return NULL;
}
Note list_delete_highest.c uses the following familiar data type:
struct node {
struct node *next;
int data;
};
delete_highest is given one argument, head
headis the pointer to the first node in a linked list
Add code to delete_highest so that it deletes the all nodes in the linked
list whose data field are equal to the highest data value in the list
delete_highest should return a pointer to the new list
If the list is now empty delete_highest should return NULL
delete_highest should call free to free the memory of any node it deletes
For example if the linked list contains these 8 elements:
16, 7, 8, 19, 13, 19, 2, 12
delete_highest should return a pointer to a list with these elements:
16, 7, 8, 13, 2, 12
Testing
list_delete_highest.c also contains a main function which allows
you to test your delete_highest function
This main function:
- converts the inputs to a linked list,
- assigns a pointer to the first node in the linked list to
head, - calls
delete_highest(head)and - prints the result.
Do not change this main function. If you want to change it, you have misread
the question.
Your delete_highest function will be called directly in marking. The main
function is only to let you test your delete_highest function
Examples
dcc list_delete_highest.c -o list_delete_highest ./list_delete_highest Total numbers in list: 8 16 7 8 19 13 19 2 12 [16, 7, 8, 13, 2, 12] ./list_delete_highest Total numbers in list: 5 200 150 27 200 200 [150, 27] ./list_delete_highest Total numbers in list: 5 4 6 2 4 6 [4, 2, 4] ./list_delete_highest Total numbers in list: 1 42 [] ./list_delete_highest Total numbers in list: 0 []
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications
delete_highestshould callfreeto free the memory for any nodes it deletesdelete_highestshould not change the data fields of list nodesdelete_highestshould not use arraysdelete_highestshould not callmallocdelete_highestshould not call scanf (orgetcharorfgets)delete_highestshould not print anything. It should not callprintf
Do not change the supplied main function. It will not be tested or marked.
1511 style list_delete_highest.c
When you think your program is working,
you can use autotest
to run some simple automated tests:
1511 autotest list_delete_highest
When you are finished working on this exercise,
you must
submit your work by running give:
give cs1511 lab09_list_delete_highest list_delete_highest.c
You must run give
before Monday 15 April 20:00
to obtain the marks for this lab exercise.
Note that this is an individual exercise,
the work you submit with give must be entirely your own.
Exercise
(●●●)
:
Determine whether a list of lists contains a diagonal line of identical values
Download lists_diagonal.c here
Or, copy these file(s) to your CSE account using the following command:
1511 fetch-activity lists_diagonal
Your task is to add code to this function in lists_diagonal.c:
// Treat the linked lists like they're a 2D array
// and return 1 if the first element is repeated
// diagonally through the lists
int has_diagonal(struct list_node *head) {
return 0;
}
lists_diagonal.c is written using struct node and struct list_node that
cannot be changed.
struct node is a normal linked list node while struct list_node is used to
make a linked list where each element contains a list of struct nodes.
For this exercise, you will implement the function has_diagonal It should
take a pointer to the head of a struct list_node linked list, and check the
values of the inner struct node linked list.
Imagine each struct node list as extending out from each struct list_node
list (i.e. a 2D linked list). has_diagonal will return 1 if there is a
diagonal pattern, and 0 if there isn't.
A diagonal in this exercise means that the first number in the first list is the same as the second number in the second list and the third number in the third list and so on.
For example if the list of lists looks like this:
list_node 0 contains the list {5, 0, 0}
list_node 1 contains the list {0, 5, 0}
list_node 2 contains the list {0, 0, 5}
has_diagonal should return 1 as the number 5 is repeated diagonally down
the list of lists:
list_node 0 contains the list {5, 0, 0}
list_node 1 contains the list {0, 5, 0}
list_node 2 contains the list {0, 0, 5}
However, if the list of lists looks like this:
list_node 0 contains the list {5, 0, 0, 0}
list_node 1 contains the list {0, 4, 0, 0}
list_node 2 contains the list {0, 0, 5, 0}
list_node 3 contains the list {0, 0, 0, 5}
has_diagonal should return 0, because the 2nd element of the second list
does not equal the value of the first element of the first list:
list_node 0 contains the list {5, 0, 0, 0}
list_node 1 contains the list {0, 4, 0, 0}
list_node 2 contains the list {0, 0, 5, 0}
list_node 3 contains the list {0, 0, 0, 5}
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications
struct nodeandstruct list_nodecannot be edited. They must be used as they are- You may not use arrays in this solution. Arrays are not necessary to complete this task
- You can assume that you'll never receive an empty list of
struct list_nodes - You can assume that all lists of
struct nodes are also not empty - You can assume that there will always be the same number of
struct nodes in each list and that will be the same number ofstruct list_nodes. That is to say, the 2D grid formed by the lists will always be square - Your submitted file may contain a
mainfunction. It will not be tested or marked
1511 style lists_diagonal.c
When you think your program is working,
you can use autotest
to run some simple automated tests:
1511 autotest lists_diagonal
When you are finished working on this exercise,
you must
submit your work by running give:
give cs1511 lab09_lists_diagonal lists_diagonal.c
You must run give
before Monday 15 April 20:00
to obtain the marks for this lab exercise.
Note that this is an individual exercise,
the work you submit with give must be entirely your own.
Exercise
(●●●)
:
Play the Game of Chairs. Win or die.
Download musical_chairs.c here
Or, copy these file(s) to your CSE account using the following command:
1511 fetch-activity musical_chairs
Your task is to add code to this function in musical_chairs.c:
// Make music for a certain number of turns.
// Each turn of music makes the players move
// one chair along the list.
// After they've moved that many times, the
// first chair in the list is removed, along
// with the person sitting in it.
struct chair *make_music(int turns, struct chair *chairs) {
// IMPLEMENT THIS FUNCTION
return chairs;
}
Welcome to the Game of Chairs, where you either win or have your memory freed.
musical_chairs is written using the following structs that cannot be changed:
// player in the game of chairs
struct player {
char name[MAX_NAME_LENGTH];
};
// A node in a linked list of chairs
struct chair {
struct player *sitting;
struct chair *next;
};
The chair struct is a linked list node.
The player struct represents a player that can sit on a chair (represented by
the chair's pointer aiming at the player).
make_music is given a pointer to a chair, which is the first element in a
list of chairs. It is also given an int turns which represents how many turns
of movement there will be before the music stops.
Like the game of Musical Chairs, this program will have players move along the linked list, changing which chair they're sitting in.
In make_music, every player moves turns spaces along the linked list.
Anyone who moves off the end of the linked list, should then move to the head
of the list, so the players will end up rotating through the list as if it's a
loop. This would be similar to if the next of the last chair was aimed at the
first chair.
Once all the players have finished moving, the head of the list of chairs is
removed. This means both that chair and the player sitting in it are removed
from the game. make_music should then print out the name of the player that
was removed.
Be careful to make sure you free all memory used in this game!
For example if a list of chairs called thrones looks like this:
throne points at the player named "Spoiler Alert" throne points at the player named "Eddard Stark" throne points at the player named "Joffrey Baratheon" throne points at the player named "Cersei Lannister" throne points at the player named "Robert Baratheon"

Then the following function is called:
make_music(3, thrones);
The output would be:
Joffrey Baratheon
and the resulting linked list would look like this:
(throne pointed at "Joffrey Baratheon" but was removed) throne points at the player named "Cersei Lannister" throne points at the player named "Robert Baratheon" throne points at the player named "Spoiler Alert" throne points at the player named "Eddard Stark"
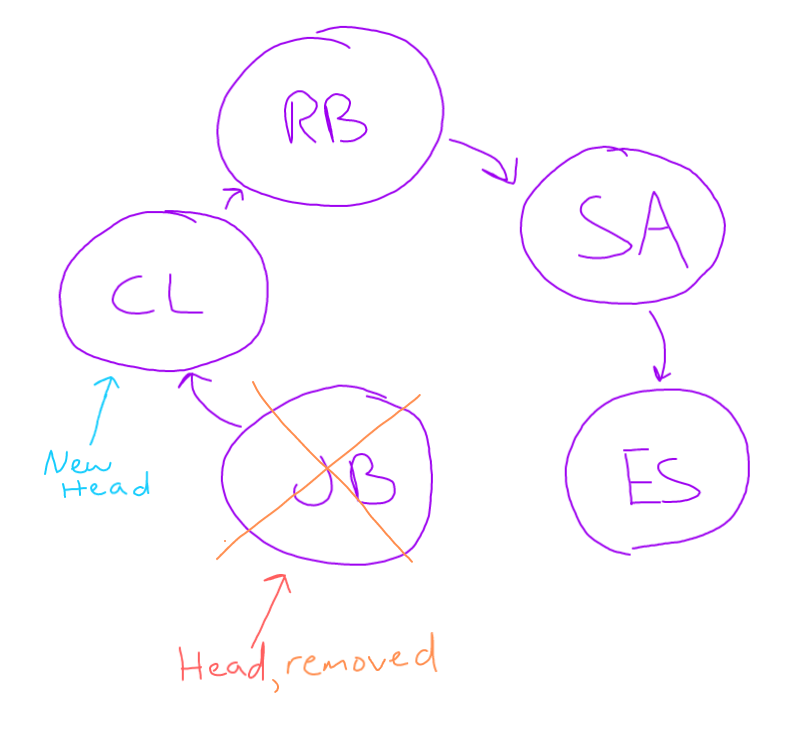
In this list, all the players have moved down 3 chairs and are now sitting in different chairs. Anyone that moved past the end of the chairs was moved back to the top of the list of chairs.
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications
- You can assume the list provided to
make_musicwill not be empty. - You can assume the number of turns will not be negative.
struct playerandstruct chaircannot be edited. They must be used as they are.- The
be_seatedfunction will help you create chairs. It cannot be edited and must be used as it is. You may not use arrays in this solution. Arrays are not necessary to complete this task. - You must free all memory used in your program. Use
dcc --leak-checkif you need to check for memory leaks. Autotest will also check your code for leaks - Your submitted file may contain a
mainfunction. It will not be tested or marked.
1511 style musical_chairs.c
When you think your program is working,
you can use autotest
to run some simple automated tests:
1511 autotest musical_chairs
When you are finished working on this exercise,
you must
submit your work by running give:
give cs1511 lab09_musical_chairs musical_chairs.c
You must run give
before Monday 15 April 20:00
to obtain the marks for this lab exercise.
Note that this is an individual exercise,
the work you submit with give must be entirely your own.
Exercise
(☠)
:
The Student Becomes The Teacher
Welcome to Week 9 of COMP1511. The end of term is in sight!
If you've come this far in this week's lab, you're probably feeling pretty confident in some aspects of the course! So, why not help yourself and your peers by creating a resource that teaches a concept in COMP1511?
Details
For this exercise, create content that helps teach a concept in COMP1511. This could be a video, a program, a blog, or anything else you can think of.
If you're not sure what to do, chat to your tutor for inspiration!
(When you're done, post your creation on the forum.)[https://edstem.org/au/courses/9913/discussion/]
We may also post some of the resources you share in one place, so everyone can benefit from them!
If you're interested in becoming a tutor for a COMP course, this can also be great practice, as one requirement we have for tutoring applicants is making a short explainer video.
This is the last challenge exercise for the term! Next week, we will have this exercise as well; so you'll have two weeks to complete this :)
Exercise — individual:
(Not For Marks) Debugging - List remove nth
Download debug_remove_nth.c here
Or, copy these file(s) to your CSE account using the following command:
1511 fetch-activity debug_remove_nth
Note that this exercise is not marked or worth marks!
Debugging Tips!
Some debugging tips for you:
- dcc output - as you run into issues, dcc will point you to where the errors are. Remember that dcc gives you the line number the issue is on, and will give some sort of explanation. Make sure you read everything dcc gives you. Sometimes we get “errors carried forward”, so find your first error, fix that, then recompile.
- print statements - sometimes it can be handy to see if the flow of your code puts you in the spot you expect it to be (ie. inside the right if statement, or going through a loop the correct amount of times). A quick way you can check this is by putting print statements in your code for testing purposes, like
"the value of x is %d and y is %d". This lets you check that you got against what you expected. - COMP1511 debugging guide
The Task
This task takes in a linked list via command line arguments. Prompts the user to input the index n of the node which they wish to remove form the list. Then, the program attempts to remove the node at index n via calling the delete_nth function.
For example if the existing list is 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4-> X, if the user inputs 2 as the index of the node they wish to delete after calling the delete_nth function on the list is as follows: 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> X. Note, the node containing the value 3 is removed from the list since is the node at index 2 in the original list. Note we start counting indexes from 0.
Currently it has some issues it is your job to figure them out and fix the code. Note, you should only need to modify the delete_nth function to fix the program.
Examples
dcc debug_remove_nth.c -o debug_remove_nth ./debug_remove_nth 1 2 3 4 5 6 What is the position of the node you wish to remove: 2 Original list: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] Modified list: [1, 2, 4, 5, 6] ./debug_remove_nth 1 2 3 What is the position of the node you wish to remove: 0 Original list: [1, 2, 3] Modified list: [2, 3] ./debug_remove_nth 1 2 3 4 5 What is the position of the node you wish to remove: 4 Original list: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] Modified list: [1, 2, 3, 4] ./debug_remove_nth 1 What is the position of the node you wish to remove: 0 Original list: [1] Modified list: [] ./debug_remove_nth What is the position of the node you wish to remove: 0 Original list: [] Modified list: [] ./debug_remove_nth 1 2 3 4 What is the position of the node you wish to remove: 4 Original list: [1, 2, 3, 4] Index out of range, no node deleted Modified list: [1, 2, 3, 4] ./debug_remove_nth 1 2 3 4 What is the position of the node you wish to remove: -1 Original list: [1, 2, 3, 4] Index out of range, no node deleted Modified list: [1, 2, 3, 4]
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications
- You may assume all command line arguments will be integers
- The function prints
Index out of range, no node deletedif the index entered by the user is greater then the legnth of the list. It then also does not modify the list.
Walkthrough
Below is a video walkthrough of this exercise! Make sure to attempt it before watching this video
1511 style debug_remove_nth.c
When you think your program is working,
you can use autotest
to run some simple automated tests:
1511 autotest debug_remove_nth
Submission
give.
You can run give multiple times.
Only your last submission will be marked.
Don't submit any exercises you haven't attempted.
If you are working at home, you may find it more convenient to upload your work via give's web interface.
Remember you have until Week 10 Monday 20:00 to submit your work.
You cannot obtain marks by e-mailing your code to tutors or lecturers.
You check the files you have submitted here.
Automarking will be run by the lecturer several days after the submission deadline,
using test cases different to those autotest runs for you.
(Hint: do your own testing as well as running autotest.)
After automarking is run by the lecturer you can view your results here. The resulting mark will also be available via give's web interface.