| COMP3311 25T1 |
Assignment 1 Data Models for Cheese Database |
Database Systems |
Last updated: Sunday 2nd March 8:14am
Most recent changes are shown in red ... older changes are shown in brown.
Most recent changes are shown in red ... older changes are shown in brown.
[Assignment Spec] [Database Design] [Examples] [Testing]
Introduction
This gives both an overview and a detailed description of the cheese database for this assignment. The overview is expressed as an ER diagram; the details are given via an SQL schema.
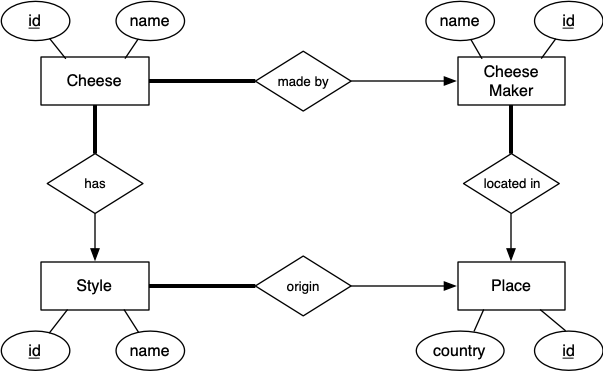
ER Model of Cheese DB
Most entities have an ID field as the primary key. We wouldn't normally show this at the ER level. We are showing only minimal attributes to avoid cluttering the ER diagram;see the SQL schema for all attributes.
Relationships between entities
Notes:
- every cheese is made by some cheesemaker
- every cheese is made according to a particular style
- we know at least the country where each cheesemaker is located
- we know at least the country where each cheese style originated
SQL Schema for Cheese database
Notes:
- 1:n relationships are implemented by a foreign key attribute
- new types and domains aim to provide more readable table definitions
- interval values are used to represent durations of time for aging
schema.sql
-- COMP3311 25T1 Assignment 1 Database Schema
-- cheese hardness values
create type HardVal as enum ('soft','semi-soft','semi-hard','hard');
-- types of milk used in cheese making
create type MilkVal as enum ('cow','goat','sheep','buffalo','yak');
-- used for percentage of fat in cheese; higher is less healthy
create domain Percentage integer check (value between 0 and 100);
create domain YearVal integer check (value between 1000 and 3000);
-- we always know the country, but may not know the region or town
create table Places (
id integer,
country text not null,
region text,
town text,
primary key (id)
);
-- in PostgrSQL intervals, "months" are denoted "mons"
-- cheeses need to be aged for at least 1 day
create table Styles (
id integer,
name text not null unique,
hardness HardVal not null,
milk MilkVal not null,
notes text,
min_aging interval not null,
max_aging interval not null,
fat Percentage not null,
origin integer not null references Places(id),
primary key (id)
);
create table Makers (
id integer,
name text not null,
located_in integer not null references Places(id),
founded YearVal,
primary key (id)
);
-- cheese names do not have to be unique
-- maybe two cheesemakers have a cheese called "Vintage Cheddar"
create table Cheeses (
id integer,
name text not null,
style integer not null references Styles(id),
aged_for interval not null,
fat Percentage not null,
notes text,
made_by integer not null references Makers(id),
primary key (id)
);