| COMP3311 22T3 |
Assignment 1 Data Models for BeerDB |
Database Systems |
Last updated: Saturday 24th September 1:46pm
Most recent changes are shown in red ... older changes are shown in brown.
Most recent changes are shown in red ... older changes are shown in brown.
[Assignment Spec] [Database Design] [Examples] [Testing] [Submitting] [Fixes+Updates]
Introduction
This gives both an overview and a detailed description of the beer database for this assignment. The overview is expressed as an ER diagram; the detail is give via an annotated SQL schema.
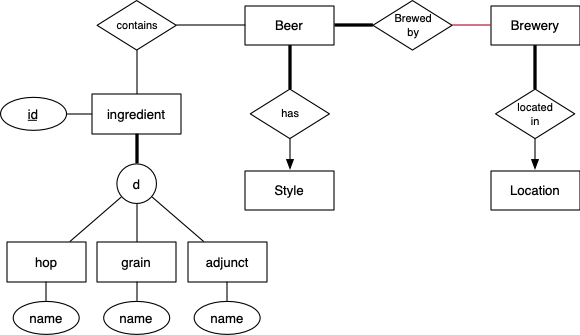
ER Model of BeerDB
Most entities have an ID field as the primary key. We wouldn't normally do this at the ER level, but none of the entities seemed to have obvious and compact primary keys.
Relationships between entities
Notes:
- every beer is brewed by some brewery
- several breweries may collaborate on one beer
- every beer is associated to a style
- the ingredients class hierarchy as a bit contrived, but would be useful if we wanted different information for each of the different type of ingredient (e.g. colour for grains)
- sometimes we may not know the ingredients in a beer
- we know at least the country where each brewery is located
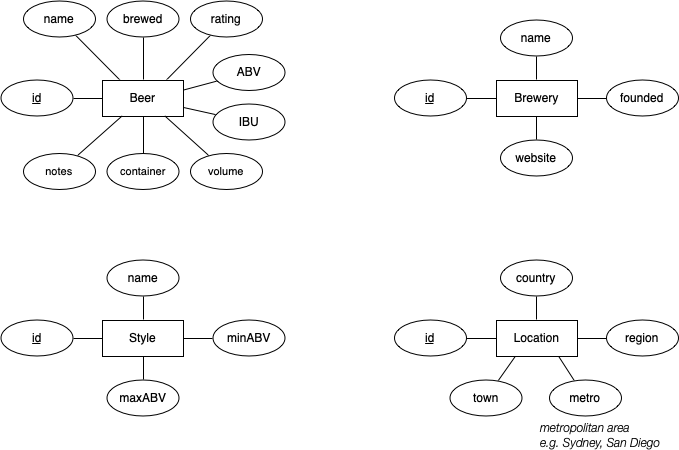
Attributes of entities
SQL Schema for BeerDB
Notes:
- n:m relationships are implemented by a new table
- 1:n relationships are implemented by a FK attribute
- the Ingredients class hierarchy is implemented by the single-table mapping
- new types and domains aim to provide more readable table definitions
schema.sql
-- BeerDB Schema
-- Original version: John Shepherd (Sept 2021)
-- Current version: John Shepherd (Sept 2022)
--
-- To keep the schema a little shorter, I have ignored my usual
-- convention of putting foreign key definitions at the end of
-- the table definition.
--
-- Some general naming principles:
-- max 10 chars in field names
-- all entity tables are named using plural nouns
-- for tables with unique numeric identifier, always call the field "id"
-- for cases where there's a long name and a short name for something,
-- use "name" for the short version of the name (typically for display),
-- and use "longname" for the complete version of the name (which might
-- typically be used in lists of items)
-- for foreign keys referring to an "id" field in the foreign relation,
-- use the singular-noun name of the relation as the field name
-- OR use the name of the relationship being represented
--
-- Null values:
-- for each relation, a collection of fields is identified as being
-- compulsory (i.e. without them the data isn't really usable) and
-- they are all defined as NOT NULL
-- reminder: all of the primary keys (e.g. "id") are non-NULL
-- note also that fields that are allowed to be NULL will need to be
-- handled specially whenever they are displayed e.g. in a web-based
-- interface to this schema
--
-- Types/Domains
create type IngredientType as enum ('hop','grain','adjunct');
create type ContainerType as enum ('bottle','can','growler','keg');
create domain YearValue as integer check (value between 1000 and 2100);
create domain MilliLiters as integer check (value > 0);
create domain URLvalue as text check (value like '%.%'); -- weak check
create domain ABVvalue as real check (value between 0.0 and 100.0);
create domain IBUvalue as integer check (value between 0 and 200);
-- Tables
create table Locations (
id integer, -- would normally use serial
country text not null, -- must at least know country
region text, -- state or shire or ...
metro text, -- metroploitan area (e.g. Sydney)
town text, -- in metro area => suburb, outside metro => town
primary key (id)
);
create table Styles (
id integer, -- would normally use serial
name text not null, -- name of style (e.g. lager, IPA)
min_abv ABVvalue not null,
max_abv ABVvalue not null,
primary key (id),
constraint minmax check (min_abv <= max_abv)
);
create table Ingredients (
id integer, -- would normally use serial
itype IngredientType not null,
name text not null,
primary key (id)
);
create table Breweries (
id integer, -- would normally use serial
name text not null,
founded YearValue,
website URLvalue,
located_in integer not null references Locations(id),
primary key (id)
);
create table Beers (
id integer, -- would normally use serial
name text not null,
brewed YearValue,
style integer not null references Styles(id),
ABV ABVvalue not null,
IBU IBUvalue,
sold_in ContainerType,
volume MilliLiters,
notes text,
rating integer not null check (rating between 0 and 10),
primary key (id)
);
create table Contains (
beer integer references Beers(id),
ingredient integer references Ingredients(id),
primary key (beer,ingredient)
);
create table Brewed_by (
beer integer references Beers(id),
brewery integer references Breweries(id),
primary key (beer,brewery)
);