Programming Fundamentals
Recursion
Warning: This challenge is very hard. The provided solution uses a technique called recursion, that is covered early in COMP2521. Students looking for a challenge have lots to gain from completing this challenge. Recursion occurs when a function calls itself in order to solve smaller sub problems of an overall problem, until it reaches a base case that does not require recursion to calculate.
Below is an example program that finds the Nth fibonacci number using recursion. If you are unfamiliar with the Fibonacci sequence please see here
#includeint fib(int n) { if (n == 0 || n == 1) { // Base case return n; } // Recursive case return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2); } int main (void) { int n = 0; scanf("%d", &n); printf("The %d(th|nd|st) Fibonacci number is %d\n", n, fib(n)); return 0; }
If we consider the case where n = 4, we can build out what is called a recursion tree.
In this tree, the numbers on the edges signify the order in which the functions are called. These functions are resolved in reverse order, returning the their base values (0 or 1) back up to the functions that called them, until fib(4) is resolve to equal 3.
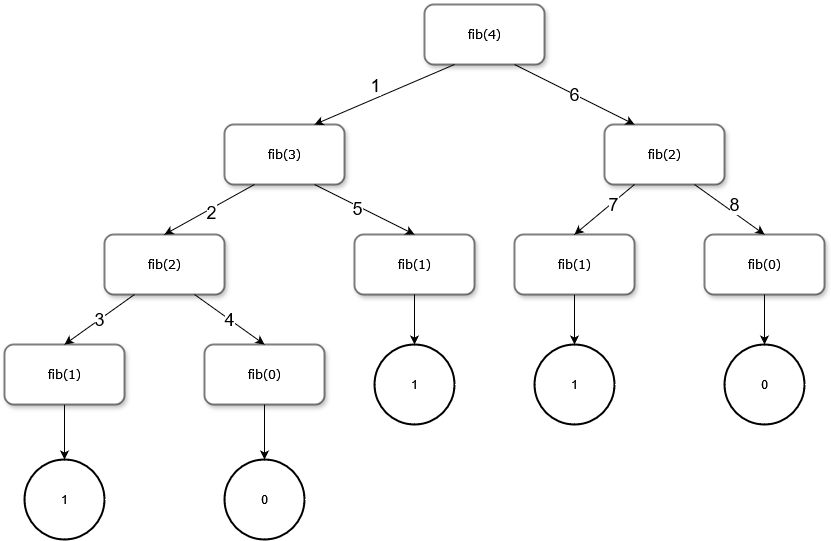
Another representation of this is:
fib(4) = fib(3) + fib(2)
= (fib(2) + fib(1)) + fib(2)
= ((fib(1) + fib(0)) + fib(1)) + fib(2)
= ((fib(1) + fib(0)) + 1) + fib(2)
= ((1 + 0) + 1) + fib(2)
= ((1 + 0) + 1) + (fib(1) + fib(0))
= ((1 + 0) + 1) + (1 + 0)
= 3
Note: If you do not have a correct/reliable base case, your recursion will continue indefinitely, using up all the memory allocated to the program. This will cause an error called a stack overflow. For more info see here
For the curious student: Another cool use for recursion is to run operations on linked lists. Just beware of causing a stack overflow when your linked list is too big!
Challenge
Write a program that finds attempts to find a solution to a Sudoku puzzle. If there is no solution the program should return "No solution found!".
Examples:
Solution found:
dcc sudoku.c -o sudoku ./sudoku Enter values: 5 3 0 0 7 0 0 0 0 6 0 0 1 9 5 0 0 0 0 9 8 0 0 0 0 6 0 8 0 0 0 6 0 0 0 3 4 0 0 8 0 3 0 0 1 7 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 6 0 6 0 0 0 0 2 8 0 0 0 0 4 1 9 0 0 5 0 0 0 0 8 0 0 7 9 Solution found! 5 3 4 6 7 8 9 1 2 6 7 2 1 9 5 3 4 8 1 9 8 3 4 2 5 6 7 8 5 9 7 6 1 4 2 3 4 2 6 8 5 3 7 9 1 7 1 3 9 2 4 8 5 6 9 6 1 5 3 7 2 8 4 2 8 7 4 1 9 6 3 5 3 4 5 2 8 6 1 7 9
No solution found:
dcc sudoku.c -o sudoku ./sudoku Enter values: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 6 0 3 0 0 5 0 0 9 0 0 0 2 0 0 8 0 0 7 0 0 8 0 0 0 0 6 0 0 1 0 3 4 5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 8 0 0 4 0 0 2 1 6 7 0 0 5 0 0 4 3 0 0 0 No solution found!