2D Arrays
Week 5 Lab Exam
- This course has an invigilated final exam
- To prepare you on the format, we are having a week 5 in-lab exam
- Please attend your week 5 lab as scheduled
Worth 1 mark
https://buytickets.at/comp1511unsw/1741784
Access code is COMP1511
Email course account if you can't attend
Strings recap
- An array of chars
- We have a single identifier for the string
- Anything we can do with arrays, applies
char[]
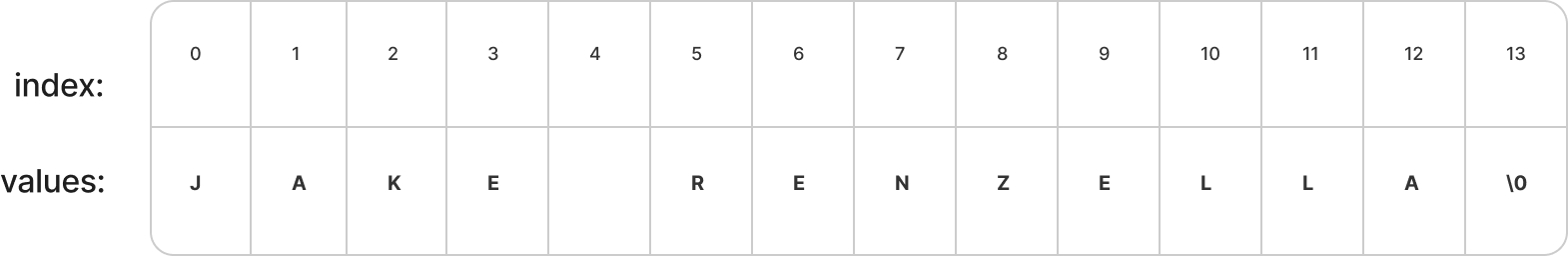
Notice the \0 at the end! This means that C will know when it reaches the end of the array
Note the # of elements, and don't forget the \0
String literals
"Jake!"
- uses double quotes
"to wrap the string literal - single quote for characters!
Used to assign strings to
char[]easily:char name[] = "Jake Renzella";
Useful string functions
fgets()-> reads a stringfputs()-> prints a stringstrlen()-> gives us the length of the string (excluding the\0).strcpy()-> copy the contents of one string to anotherstrcat()-> join one string to the end of another (concatenate)strcmp()-> compare two strings
note: some of these may requirestrchr()-> find the first occurrence of a character#include <string.h>
Reassigning a string
int main(void) {
char name[MAX_LEN] = "Jake";
strcpy(name, "Mr Otterington");
}
^ Remember we can't reassign like:
name = "Mr Otterington";
Arrays of Structs
Concept Introduction
Structs
- Structs allow us to store groupings of data
- We define structs above main and specify each field's type
- We use the
.operator to access the field once we initialise a struct!
Arrays
- We can create arrays to store multiples of data
- They are homogenous, so can only store the same type
We can have arrays of type (char, int, struct, enum)
Structs 🤝 Arrays?
Yes!
Array of structs
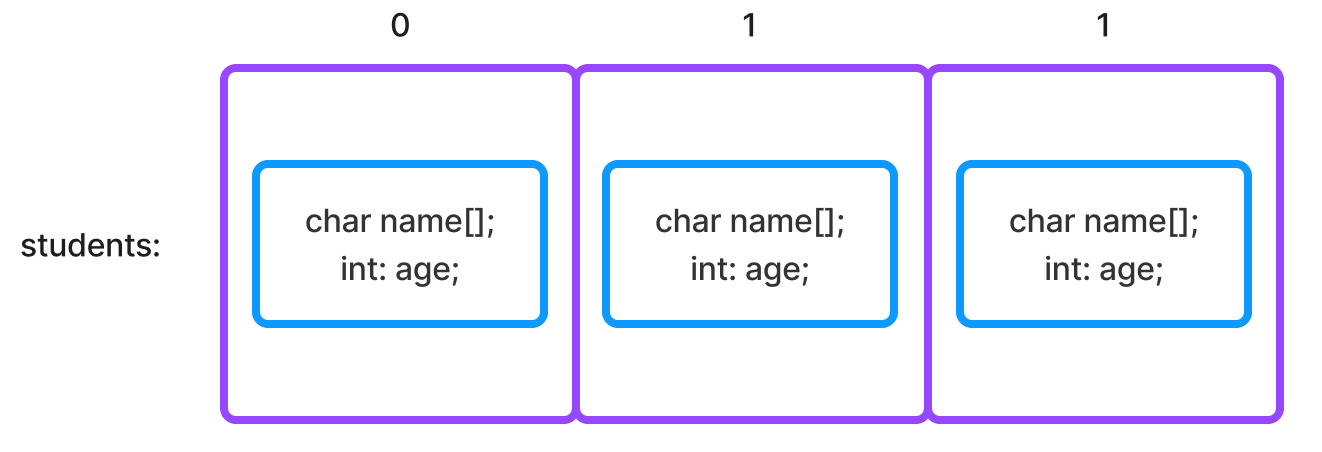
- Use
students[1].name;to access element 1's name
2D arrays
Array of arrays
2D arrays
<type> <identifier>[<rows>][<cols>];
int my_grid[5][5];
my_grid[2][3];
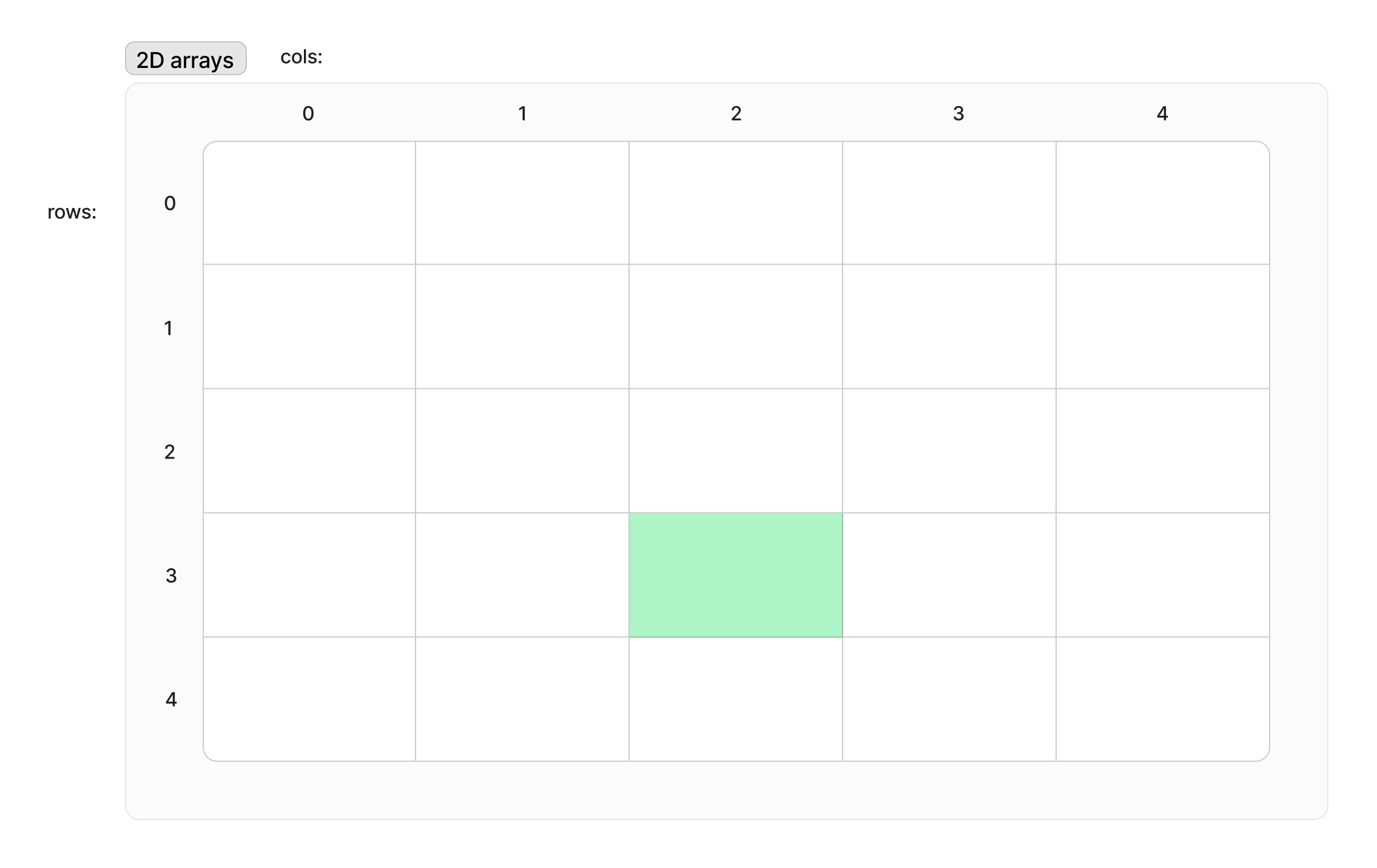
Visualisation
Large demo Program
- An array of array of structs
- Battleships? Naughts and Crosses?
