COMP(1511|1911) 25T2 Prac Exam
Time allowed: 3 hours and 10 minutes (10 minutes reading time, 3 hours working time)
Total number of questions: 11
Total number of marks: 100
Questions are NOT worth the same amount of marks
The distribution of marks is as follows:
- Questions 1 and 3: 12 marks each (LINKED LISTS HURDLES)
- Questions 2 and 4: 12 marks each (ARRAY HURDLES)
- Questions 5 - 8: 5 marks each
- Questions 9 - 10: 11 marks each
- Question 11: 10 marks
Attempt all questions
You should keep this paper confidential. Sharing it, DURING or AFTER the exam is prohibited.
Paper Information
Exam Condition Summary
- The exam paper is confidential, sharing it or its contents after the exam is prohibited.
- Even after you finish the exam, until all exams have concluded, do NOT communicate your exam answers to anyone. Some students may still be yet to sit the exam.
- Do NOT recreate your exam work in any location, including file sharing services such as Dropbox or GitHub, accessible to any other person.
- Your zpass should NOT be disclosed to any other person. If you have disclosed your zpass, you should change it immediately.
- You are allowed to use any resources available in the exam environment (e.g course website, or linux
manpages) during the exam.
Exam Hurdle Requirement
COMP1911 Assessment Students
The course has ONE hurdle in the final exam that you must meet to pass the course:
- An array hurdle – you must pass at least one of the two array questions (the two questions are clearly marked in the exam as array hurdles);
Please note, you are NOT required to pass the Linked list hurdle to pass COMP1911.
COMP1511 Assessment Students
The course has TWO hurdles in the final exam that you must meet to pass the course:
- An array hurdle – you must pass at least one of the two array questions (the two questions are clearly marked in the exam as array hurdles);
- A linked list hurdle - you must pass at least one of the two linked list questions (the two questions are clearly marked in the exam as linked list hurdles).
Exam Environment
- The exam comes with its own starter files. These files will be present in your home directory when you log in to the exam.
- At the start of the exam, there will be 10 minutes of reading time. You may not write code, or write on the provided paper during this time.
- You may submit your answers, using the
submitcommand:submit prac_qX(whereXis the question number). - You must write all of your code for each question in that question's corresponding
.cfile. Multi-file programs will not be accepted in submission. - You can submit as many times as you wish. Only the last submission will be marked.
- Do NOT leave it to the deadline to submit your answers. Submit each question when you finish working on it.
- Please make sure that you submit all your answers at the conclusion of the exam – running the autotests does not automatically submit your code.
- Autotests are available for all questions to assist in your testing, you can use the command (where X is the question number):
autotest prac_qX - Passing autotests does not guarantee full marks. Remember to do your own testing!
- No marks are awarded for style – but use reasonable formatting so the marker can read your code/answer.
- No marks are awarded for commenting – but you can leave comments for the marker to make your code more legible as needed.
Language Restriction
- All programming questions must be answered entirely in C. You may not use other programming languages.
- You are not permitted to use functions from C libraries other than the standard libraries.
- Individual questions may specify C features that you are NOT permitted to use, or C functions that you are NOT permitted to use. Please pay careful attention to the questions.
- Your C program cannot run external programs, e.g. it cannot call the function
system() - You cannot use the -l option to dcc
Fit to Sit
By sitting or submitting an assessment on the scheduled assessment date, a student is declaring that they are fit to do so and cannot later apply for Special Consideration.
If, during an exam you feel unwell to the point that you cannot continue with the exam, you should raise you hand and inform an invigilator, who will provide advice as to the best course of action.
Technical Issues
If you experience a technical issue, you should raise your hand and wait for an invigilator to assist.
Questions
Question 1
(●◌◌◌)
:
Passing this question, or question 3, is sufficient to pass the linked lists hurdle.
(12 marks)1511 fetch-prac prac_q1
Note prac_q1.c uses the following familiar data type:
struct node {
struct node *next;
int data;
};
The function first_prime takes one argument, head, where head is a pointer to the first node of a linked list.
The function should return the first prime number in the list, if there is one. If there are no prime numbers in the list, the function should return -1.
A prime number is a whole number that is only exactly divisible (leaving no remainder) by 1 and the number itself.
For example, suppose the linked list contains the following values:
4 -> 11 -> 7 -> 9 -> XThe function
first_prime should return the value 11 in the linked list, which is the first prime number in the list.
For example, suppose the linked list contains the following values:
4 -> 4 -> 4 -> XThe function
first_prime should return the value -1, as there are no prime numbers in the list.
Testing
prac_q1.c also contains a main function which allows you to test your first_prime function.
This main function:
- converts the command-line arguments to a linked list,
- assigns a pointer to the first node in the linked list to
head, - calls
first_prime(head), - prints the result.
Do not change this main function. If you want to change it, you have misread the question.
Your first_prime function will be called directly in marking. The main function is only to let you test your first_prime function
Here is how the main function allows you to test first_prime:
dcc prac_q1.c -o prac_q1 ./prac_q1 10 4 15 17 17 ./prac_q1 5 64 15 99 25 5 ./prac_q1 1 9 -1 ./prac_q1 16 -1 ./prac_q1 2 3 5 2
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications.
- The value 1 is not considered to be a prime number.
- Do not change the definition of struct node.
first_primeshould return -1 if the list is empty.first_primeshould return only a single integer.first_primeshould not change the linked list it is given.first_primeshould not change the next or data fields of list nodes.first_primeshould not use arrays.first_primeshould not call malloc.first_primeshould not call scanf (or getchar or fgets).first_primeshould not print anything. It should not call printf.first_primedoes not need need to consider integer overflow in its calculations.- Do not change the definition of struct node.
- Do not change the supplied
mainfunction. It will not be tested or marked.
1511 autotest-prac prac_q1
Question 2
(●◌◌◌)
:
Passing this question, or question 4, is sufficient to pass the arrays hurdle.
(12 marks)1511 fetch-prac prac_q2
min_lowercase will be passed in a character array with exactly
size columns. Add code so that the
min_lowercase function returns the lowercase letter with the lowest
ASCII value.
Examples
If the array contains these elements:
{'c', 'A', 'e', 'P', '!'}
Your function should return the character 'c' because it is lowercase and has the lowest ASCII value compared to all other characters in the array.
For example if the array contains these elements:
{'O', '@', 'g'}
Your function should return the character 'g' because it is lowercase and has the lowest ASCII value compared to all other characters in the array.
Testing
prac_q2.c also contains a simple main function which allows you to test your min_lowercase function.
Your min_lowercase function will be called directly in marking.
The main function is only to let you test your
min_lowercase function.
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications.
- You can assume that the array has at least 1 lowercase letter.
- You can assume that the array will have at most 100 characters.
-
min_lowercaseshould not modify the array it is provided. -
min_lowercaseshould not call scanf (or getchar or fgets). -
min_lowercaseshould not print anything, i.e. It should not callprintf. - The provided starter code contains a main function. You can change it for your own testing, but it will not be autotested or marked.
1511 autotest-prac prac_q2
Question 3
(●●◌◌)
:
Passing this question, or question 1, is sufficient to pass the linked lists hurdle.
(12 marks)1511 fetch-prac prac_q3
Note prac_q3.c uses the following familiar data type:
struct node {
struct node *next;
int data;
};
delete_nth_even is given two arguments, head and
n. head is a pointer to the first node in a linked
list, and n is the position of the node from the start of the list, that you need to delete,
counting only even data values.
Add code to delete_nth_even so that it deletes the nth node in the list that contains an even number,
counting only the nodes with even values from the start of the list.
-
If
n > lengthwhere length is the number of nodes in the list ornis greater than the number of even nodes in the list, the first even node in the list should be deleted.
For example, if the original list was: 4, 3, 7, 2, 35, 4, 3 and
n was 2
The final list should be: 4, 3, 7, 35, 4, 3
2 was removed because 2 was the
second even node from the start of the list.
delete_nth_even should return a pointer to the head of the list.
delete_nth_even should free the node it deletes.
Testing
prac_q3.c also contains a main function
which allows you to test your delete_nth_even function.
This main function:
- converts the first argument into an integer: the position of the even node from the start of the list you need to remove,
- converts the rest of the command-line arguments to a linked list,
-
assigns a pointer to the first node in the linked list to
head, - calls
delete_nth_even(head, n), - prints the result.
Do not change this main function. If you want to change it, you have misread the question.
Your delete_nth_even function will be called directly in marking. The main
function is only to let you test your delete_nth_even function.
Examples
dcc prac_q3.c -o prac_q3 ./prac_q3 2 4 3 7 2 35 4 3 [4, 3, 7, 35, 4, 3] ./prac_q3 1 2 3 4 [3, 4] ./prac_q3 9 1 2 3 4 5 6 [1, 3, 4, 5, 6] ./prac_q3 5 10 20 30 40 50 [10, 20, 30, 40] ./prac_q3 3 10 20 30 40 50 [10, 20, 40, 50] ./prac_q3 1 1 [1] ./prac_q3 11 1 3 5 7 9 [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications.
-
You can assume that you will always be given a value for
n. -
You can assume that
nwill always be 1 or greater. - You cannot assume that the list is non-empty.
-
If
n >= lengthwhere length is the number of nodes in the list ornis greater than the number of even nodes in the list, the first even node in the list should be deleted. -
If the given list contains no even numbers,
delete_nth_evenshould not delete any nodes and leave the list unchanged. -
delete_nth_evenshould return the (possibly changed) head of the list. -
delete_nth_evenshould call free to free the memory for the node it deletes. -
delete_nth_evenshould not change the data fields of list nodes. -
delete_nth_evenshould not use arrays. -
delete_nth_evenshould not call malloc. -
delete_nth_evenshould not callscanf(orgetcharorfgets). -
delete_nth_evenshould not print anything. It should not call printf. -
Do not change the definition of
struct node. -
Do not change the supplied
mainfunction. It will not be tested or marked.
If you get this autotest message:
Error: free not called for memory allocated with malloc in ...
You have not freed a node you have deleted.
1511 autotest-prac prac_q3
Question 4
(●●◌◌)
:
Passing this question, or question 2, is sufficient to pass the arrays hurdle.
(12 marks)1511 fetch-prac prac_q4
vowels_exactly_balanced will be passed an array of strings, with
exactly size strings. Each row contains a string terminated by the
null terminator ('\0') character. Write the
vowels_exactly_balanced function which returns 1 if each string
contains exactly the same number of vowels, or 0 if they do not.
Examples
If the array contains these elements:
{'a', 'a', 'a', 'a', '\0'},
{'c', 'o', 'm', 'p', '\0'},
{'o', 'o', 'o', 'h', '\0'},
{'y', 'a', 'y', 'a', '\0'},
Your function should return false (0), since each string does not have the same number of vowels.
For example if the array contains these elements:
{'a', 'b', 'c', '\0'},
{'!', 'e', '\0'},
{'a', 'c', '\0'},
Your function should return true (1), since each string contains 1 vowel.
For example if the array contains these elements:
{'f', 'g', 'h', '\0'},
{'j', '\0'},
{'z', 'x', 'c', 'v', 'b', 'n', 'm', '\0'},
Your function should return true (1), since each string contains 0 vowels.
Testing
prac_q4.c also contains a simple
main function which allows you to test your
vowels_exactly_balanced function.
Your vowels_exactly_balanced function will be called directly in
marking. The main function is only to let you test your
vowels_exactly_balanced function.
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications.
- Uppercase and lowercase vowels all count as vowels. The vowels are 'a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u', 'A', 'E', 'I', 'O', 'U'.
-
vowels_exactly_balancedcan assume there will be at least one string - If there is one string, it will always be balanced, so return 1
- You may assume that the array will only be comprised of any ASCII characters.
- Your function should return a single integer; 0 for false, and 1 for true.
-
Each string in
vowels_exactly_balancedwill always have a null terminator character at the final position -
Each string in
vowels_exactly_balancedcontains at most 100 characters -
vowels_exactly_balancedshould not print anything. It should not call printf. - Your starter code contains a main function. You can change it for your own testing, but it will not be marked.
- You must not change the given array.
1511 autotest-prac prac_q4
Question 5
(●◌◌◌)
:
(5 marks)
1511 fetch-prac prac_q5
prac_q5.c is meant to do the following:
- Scan in an integer representing a month in the year.
- Print a message indicating the season in Australia for the entered month.
- From December through to February (12 to 2, inclusive), it is summer in Australia.
- From March to May (3 to 5, inclusive), it is autumn in Australia.
- From June to August (6 to 8, inclusive), it is winter in Australia.
- From September to November (9 to 11, inclusive), it is spring in Australia.
- If an invalid integer is entered (i.e. when month is less than 1 or greater than 12), an error message is printed.
Once fixed, your program should match the following example exactly:
dcc prac_q5.c -o prac_q5 ./prac_q5 Enter the month number (1-12): 0 Invalid month entered. ./prac_q5 Enter the month number (1-12): 12 It's summer in Australia. ./prac_q5 Enter the month number (1-12): 5 It's autumn in Australia.
There are currently a number of issues in the code that you must fix for the code to work correctly, and produce the desired output. This may include changing lines, adding lines, or removing lines. Submit your working version of the code.
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications.
- You can assume that you will be given an integer for the month.
1511 autotest-prac prac_q5
Question 6
(●◌◌◌)
:
(5 marks)
1511 fetch-prac prac_q6
extract_evens is given one arguments:
head: a pointer to the first node of a linked list.
extract_evens should create a new list containing only the nodes with even values from the input list.
The relative order of the even values in the new list must match the order **in which** they appeared in the original list.
Examples
For example, if the list contains the following values:
- original list: 3 -> 2 -> 5 -> 8 -> 6 -> 7
After calling extract_evens(head), the list evens should contain:
- 2 -> 8 -> 6
Testing
The file prac_q6.c contains a main function that allows you to test your implementation.
This main function:
- Converts command-line arguments into a linked list.
- Calls
extract_evens(head). - Prints the resulting even list on a single line.
Do not change this main function. It does not contain any bugs.
dcc prac_q6.c -o prac_q6 ./prac_q6 3 2 5 8 6 7 2 8 6 ./prac_q6 1 3 5 No even nodes ./prac_q6 0 -2 -10 -8 0 -2 -10 -8 ./prac_q6 No even nodes
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications
- Do not change the definition of
struct node. - Do not change the
mainfunction. extract_evensmust not read from input or print to output.- You may assume all numbers are integers (positive, negative, or zero).
- zero is considered to be an even number.
1511 autotest-prac prac_q6
Question 7
(●◌◌◌)
:
(5 marks)
1511 fetch-prac prac_q7
You have been provided with a file called prac_q7.c.
The code in prac_q7.c is meant to do the following:
- Take in an integer
n, as input from the user. -
Call the function
find_sum_of_square()to calculate the sum of squares from 1 ton. -
Store the resulting value in the
resultpointer variable. - Print the result in the main function.
dcc prac_q7.c -o prac_q7 ./prac_q7 Enter n: 4 The sum of squares from 1 to 4 is: 30 ./prac_q7 Enter n: 1 The sum of squares from 1 to 1 is: 1 ./prac_q7 Enter n: 6 The sum of squares from 1 to 6 is: 91
There are currently a number of issues in the code that you must fix for the code to work correctly, and produce the desired output. This may include changing lines, adding lines, or removing lines. Submit your working version of the code.
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications
- You may assume the user will always input a positive integer.
-
Your
find_sum_of_squarefunction should not print anything. - You may assume that the result will not exceed the maximum size of an integer.
1511 autotest-prac prac_q7
Question 8
(●◌◌◌)
:
(5 marks)
1511 fetch-prac prac_q8
prac_q8.c is meant to do the following:
This program should create and scan in the elements of a 3x3 2d array, then multiply all the odd numbers in the 2d array by 100.
However, it has some issues that you need to fix.Once fixed, your program should match the following example exactly:
Examples
dcc prac_q8.c -o prac_q8 ./prac_q8 Enter your numbers: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Converted: 100 2 300 4 500 6 700 8 900 ./prac_q8 Enter your numbers: 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 Converted: 100 2 300 100 2 300 100 2 300 ./prac_q8 Enter your numbers: 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 Converted: 100 100 100 2 2 2 300 300 300
There are currently a number of issues in the code that you must fix for the code to work correctly, and produce the desired output. This may include changing lines, moving lines, or removing lines. Submit your working version of the code.
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications.
1511 autotest-prac prac_q8
Question 9
(●●●◌)
:
(11 marks)
1511 fetch-prac prac_q9
Write a C program prac_q9.c which reads a single line of input (a string).
The program should then modify the string according to the following rules and print the modified string.
- For each letter in the string, increase it by the number of subsequent letters that are alphabetically greater.
- A letter is considered alphabetically greater than another if it comes later in the English alphabet (e.g.,
bis greater thana). - Letters can't go past
zorZ(depending on their starting case). For example,yZzzbecomeszZzzsinceycan only increment once before hitting the limit.
For example:
dcc prac_q9.c -o prac_q9 ./prac_q9 Original String: aBc New String: cCc ./prac_q9 Original String: zyx New String: zyx ./prac_q9 Original String: ProgrammingFUNdamentals New String: UussupssqqnMUPjgpiptcms
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications
- Your program should print the modified string followed by a newline character (
\n). - You can assume the input string contains no more than 100 characters.
- You can assume the input only contains English letters, i.e
a-zandA-Z. - You are free to write this program in any way you wish using the C language: there is no specific function that you need to implement. Note that your program will need to have a
mainfunction.
1511 autotest-prac prac_q9
Question 10
(●●●◌)
:
(11 marks)
1511 fetch-prac prac_q10
You have the goal of determining the minimum number of trains needed to travel from a source train stop to a target train stop.
In this task, you will be given input through the command line consisting of:
-
n- the number of train routes. -
A sequence of
ntrain routes, where each routeiconsists of:-
mi- the number of stops on routei. -
miintegers representing the stops on that route.
-
-
src- the source train stop. -
dest- the destination train stop.
Once the minimum number of trains is determined, the program should print
The minimum number of trains to travel from stop [src] to stop [dest] is [min_num_stops].
If there is no route from src to dest, the program should print
Stop [dest] from stop [src] is not reachable.
For example, if the command-line arguments provided were:
2 3 1 2 7 3 3 6 7 1 6n= 2m1number of stops = 3m1route = 1, 2, 7m2number of stops = 3m2route = 3, 6, 7src= 1dest= 6
- Train 1: 1, 2, 7
- Train 2: 3, 6, 7
The minimum number of trains to travel from stop 1 to stop 6 is 2.
In another example, if the command line arguments provided were:
3 3 1 2 3 3 3 4 5 2 6 7 1 7n= 3m1number of stops = 3m1route = 1, 2, 3m2number of stops = 3m2route = 3, 4, 5m3number of stops = 2m3route = 6, 7src= 1dest= 7
- Train 1: 1, 2, 3
- Train 2: 3, 4, 5
- Train 3: 6, 7
Stop 7 from stop 1 is not reachable.
as there is no route from stop 1 to stop 7.
Examples
dcc prac_q10.c --leak-check -o prac_q10 ./prac_q10 3 3 1 2 3 3 3 4 5 2 6 7 1 7 Stop 7 from stop 1 is not reachable. ./prac_q10 3 2 1 2 2 2 2 3 2 3 4 1 4 The minimum number of trains to travel from stop 1 to stop 4 is 2. ./prac_q10 2 3 1 2 3 3 3 4 5 1 8 Stop 8 from stop 1 is not reachable.
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications.
-
Your code must pass
--leak-checkwith no memory leaks. - You may assume that your will always be provided the correct amount of command line arguments.
-
You may assume that train routes will follow the path of
m1m2m3...mim1and so on. - You may assume that you will always be provided valid input.
1511 autotest-prac prac_q10
Question 11
(●●●●)
:
(10 marks)
1511 fetch-prac prac_q11
Given the coordinates and heights of all the mountains, your task is to determine the skyline formed by these mountains, which is the outline formed when all the mountains are viewed together from a distance.
The information of each mountain is provided as command line arguments in the
format:
left1 right1 height1 left2
right2 height2 ...
-
leftiis the x-coordinate of the left edge of the ith mountain. -
rightiis the x-coordinate of the right edge of the ith mountain. -
heightiis the height, or y-coordinate, of the ith mountain.
The skyline should be represented as a collection of "key point" pairs
comprising of x and y-coordinates, sorted by their x-coordinate. Your program
should print these points in the format
[[x1, y1], [x2, y2], ...]. Here, each key point pair is the left endpoint of some horizontal segment
in the skyline,
except for the last key point pair, which always has a y-coordinate of 0.
This last point is used to mark the end of the skyline, corresponding to where
the rightmost mountain ends.
- If two mountains have the same left x-coordinate, sort the resulting key points by their right x-coordinate.
- If two mountains have the same left and right x-coordinates, sort resulting key points by their y-coordinate.
The ground between the leftmost and rightmost mountains should also be included as part of the skyline's outline.
For example if you were provided the following input
2 9 10 3 7 15 5 12 12 15 20 10 19 24 8
You would interpret this as:
-
Mountain 1: [2, 9, 10]
- Starts at x = 2
- Ends at x = 9
- Height = 10
-
Mountain 2: [3, 7, 15]
- Starts at x = 3
- Ends at x = 7
- Height = 15
-
Mountain 3: [5, 12, 12]
- Starts at x = 5
- Ends at x = 12
- Height = 12
-
Mountain 4: [15, 20, 10]
- Starts at x = 15
- Ends at x = 20
- Height = 10
-
Mountain 5: [19, 24, 8]
- Starts at x = 19
- Ends at x = 24
- Height = 8
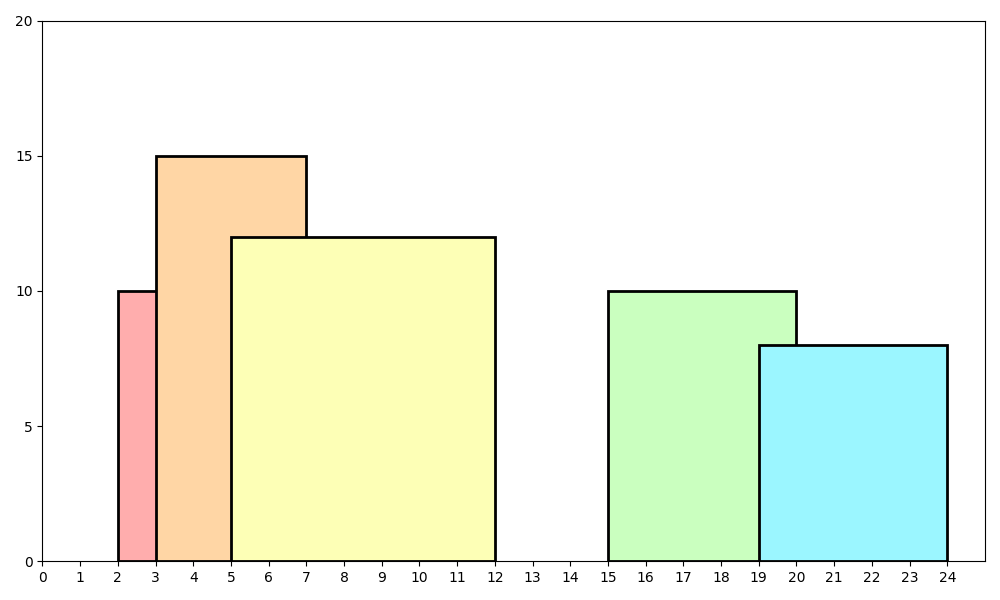
Meaning that
- at x = 2, the skyline rises to height 10
- at x = 3, the skyline rises to height 15
- at x = 7, the skyline drops to height 12
- at x = 12, the skyline drops to height 0
- at x = 15, the skyline rises to height 10
- at x = 20, the skyline drops to height 8
- at x = 24, the skyline drops to height 0.
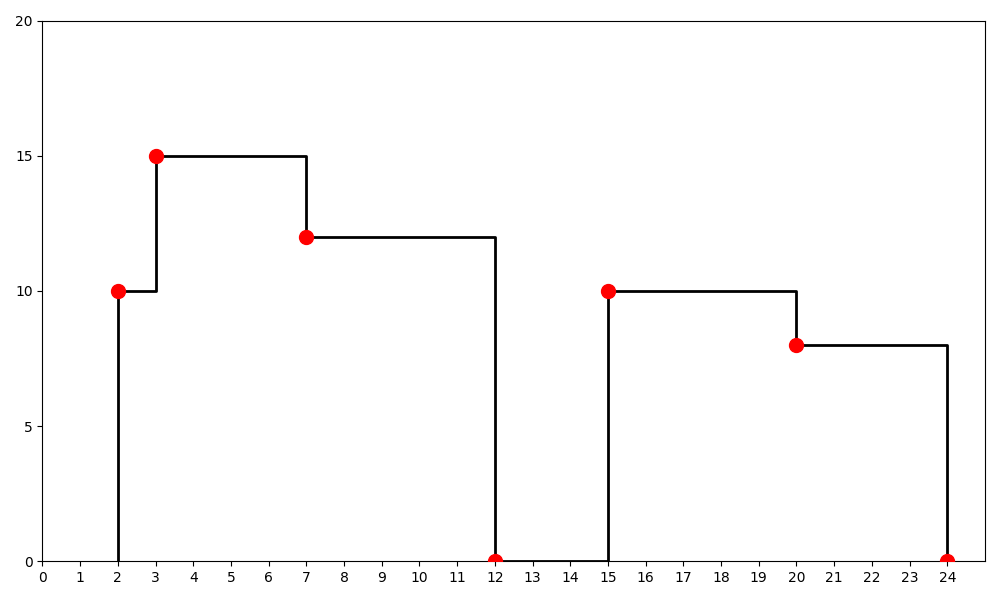
Therefore, the final key points are:
[[2, 10], [3, 15], [7, 12], [12, 0], [15, 10], [20, 8], [24, 0]]
Examples
dcc prac_q11.c --leak-check -o prac_q11 ./prac_q11 2 9 10 3 7 15 5 12 12 15 20 10 19 24 8 Skyline: [[2, 10], [3, 15], [7, 12], [12, 0], [15, 10], [20, 8], [24, 0]] ./prac_q11 1 2 1 2 3 2 3 4 3 4 5 4 Skyline: [[1, 1], [2, 2], [3, 3], [4, 4], [5, 0]] ./prac_q11 0 2 3 2 5 3 Skyline: [[0, 3], [5, 0]]
You may find the following interactive helpful for visualising skylines:
Assumptions/Restrictions/Clarifications.
- You may assume that all mountains are perfect rectangles and are grounded on a completely flat surface at height 0.
-
The width of a mountain can be 0, i.e.
leftiis the same asrighti - The height of a mountain cannot be less than or equal to 0.
- Mountains can be entered in any order.
- The ground between the leftmost and rightmost mountains should also be included as part of the skyline's outline.
- There is no maximum number of mountains.
- The program will always be provided valid input in the correct format.
-
Your code must pass
--leak-checkwith no memory leaks.
1511 autotest-prac prac_q11